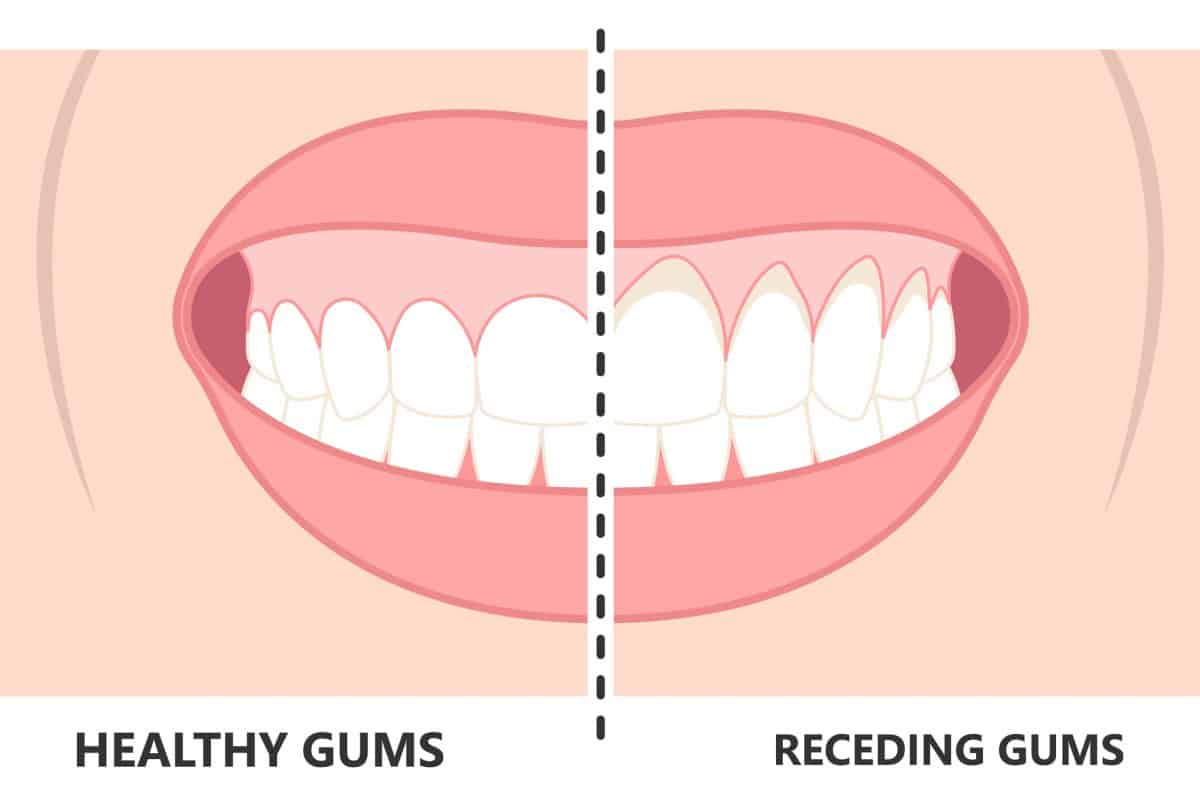
Receding gums are a common dental condition wherein the gum tissue surrounding the teeth gradually retracts, revealing more of the tooth structure.
While gum recession may seem like a purely cosmetic concern, it can lead to other problems such as increased sensitivity, tooth decay, and even tooth loss if left untreated. According to the team at Pacific Northwest Periodontics, early detection and intervention can prevent further damage to oral health.
Symptoms of Receding Gums
Symptoms of receding gums can vary, but common signs include the visible exposure of tooth roots, increased tooth sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet foods and beverages, and gum tenderness or inflammation.
Some people may experience tooth mobility or looseness, the teeth appearing longer than normal, or changes in tooth or bite alignment. If you notice any of these symptoms, consult with one of our periodontists to prevent further damage to your gums.
Gum Recession Causes
One of the primary causes of gum recession is inadequate oral hygiene practices, such as infrequent brushing and flossing. Plaque and tartar buildup along the gumline can lead to gum inflammation (gingivitis) and eventual recession of the gum tissue.
Advanced gum disease, or periodontitis, is also a leading cause of receding gums. Inflammation and infection of the gum tissue can cause it to pull away from the teeth. Left untreated, serious gum recession may result in tooth loss.
Moreover, brushing or flossing too vigorously can damage the delicate gum tissue. It can also lead to recession over time.
Some individuals may be predisposed to developing receding gums due to genetic factors. Thin or fragile gum tissue inherited from family members can increase the risk of gum recession.
Lastly, smoking or using tobacco products can contribute to gum disease and gum recession by impairing blood flow to the gums.
Gum Recession Treatment
The most common treatment to reverse gum recession is scaling and root planing. This deep cleaning technique targets and smoothes the tooth surfaces and roots of the teeth below the gum line, encouraging the gum tissue to reattach normally to the teeth. Other treatment interventions include the use of antibiotics and antibacterial mouthwash products. In the most advanced cases of gum recession, gum grafting surgery may be necessary.
Learn More About Gum Recession Treatment in Seattle, WA
If you’re concerned about receding gums, call us at (206) 575-1086 and schedule an appointment with Pacific Northwest Periodontics. Take the first step toward healthier gums and a brighter smile by booking your dental appointment today.



